UMN LakeBrowser
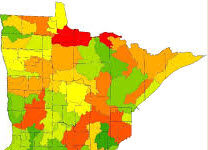
The Minnesota LakeBrowser is an online interactive lake water clarity/quality tool with Landsat-derived classifications of lake clarity of more than 10,500 lakes measured 11 times from 1975-2018. It also includes searchable statewide maps of chlorophyll concentrations and CDOM levels for several recent years. The chlorophyll classifications are based on the European Sentinel-2 satellites.
Typically, the LakeBrowser is used to find water clarity or quality information for particular Minnesota lakes. To do so, you can either zoom in and out of areas to locate the lake of interest, or search lakes by typing the lake name in the Search box. Once you have found the lake, you can display maps by year of lake clarity, chlorophyll a and CDOM, and retrieve lake information from the Minnesota Pollution Control Agency (PCA) and Department of Natural Resources (DNR).
The LakeBrowser has provided satellite derived water clarity, an indicator of lake water quality, data for over 10,000 Minnesota lakes since 2002. It has been updated with data created using an automated image processing system developed with resources from the University of Minnesota and the Environment and Natural Resources Trust Fund — Legislative and Citizens Commission on Minnesota Resources. The automated system processes all available satellite data (Landsat 8 and Sentinel 2) and provides daily (when clear imagery is available) and monthly (May – October) median clarity, chlorophyll and CDOM data for 2017 through 2020. We have also improved its capabilities for image and data display, geospatial analysis, and data access and download. For more information on remote sensing of lake water quality, our methods and results, see Remote Sensing of Water Resources.
The research and development of Satellite-based Lake Water Quality Monitoring has been by the Department of Forest Resources in collaboration with the Water Resources Center and Minnesota Supercomputing Institute. ArcGIS hosting and application development has been provided by U Spatial. Our research has been supported by the Minnesota Agricultural Experiment Station, University of Minnesota U Spatial, Minnesota Environment and Natural Resources Trust Fund — Legislative and Citizens Commission on Minnesota Resources, Minnesota Department of Natural Resources, Minnesota Pollution Control Agency, National Science Foundation, US Geological Survey, and National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
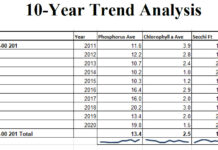
In the past year the LakeBrowser capability/functionality has been transferred to ArcGIS Server, a newer and easier to use platform that improves search and display capabilities. New data for SD, chlorophyll, turbidity and CDOM have recently been added, along with several additional enhancements, including maps and statistical analyses on distributions by ecoregion, watershed and county, plus temporal trends for clarity. Data can be downloaded by users for additional analysis.
Landsat data that have been archived at the EROS Center since Landsat 1 was launched in 1972 enable us to retrospectively classify images and examine historical trends. This type of information helps resource managers target problem areas, enables systematic monitoring of inland lakes, and demonstrates the power of satellite remote sensing. With statewide lake water clarity and quality data for more than a single time period, statistical summaries and analyses that compare conditions over time by ecoregion, watershed, and county can generated
Comments, questions or suggestions to improve the LakeBrowser? Please complete the feedback form or email us.
Sources
In addition to data created at the University of Minnesota, the following geospatial datasets were used to summarize water quality by enumeration unit (state, county, ecoregion, watershed) and, for NLCD, to display land cover in Minnesota.
- IPUMS NHGIS, University of Minnesota, www.nhgis.org, administrative boundaries (2017)
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Level III Ecoregions of the Continental United States
- Minnesota Department of Natural Resources, MNDNR Watershed Suite
- Multi-Resolution Land Characteristics Consortium (MRLC), NLCD 2016 Land Cover (CONUS)
Download Data
Vector and raster data sources used in this application are available for download on the RSGAL Data Portal and are listed below.